Every year on September 8th, the world comes together to celebrate World Physiotherapy Day, recognizing the invaluable contributions of physiotherapists in promoting health, mobility, and well-being. This day serves as a reminder of the vital role these healthcare professionals play in enhancing the lives of countless individuals. The theme of World Physical Therapy Day 2023 is “Illuminating Arthritis”. It takes center stage, highlighting the critical role of physiotherapy plays in improving the lives of millions of people living with arthritis.
The Role of Physiotherapy:
- Rehabilitation: Physiotherapists help individuals recover from injuries, surgeries or debilitating medical conditions. They design personalized rehabilitation programs to restore mobility, strength, and function.
- Pain Management: Physiotherapy is instrumental in managing pain, whether it is chronic pain, sports injuries, or post-surgery discomfort. Techniques such as manual therapy, exercise, and modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation are used to alleviate pain.
- Preventive Care: Physiotherapists work to prevent injuries and maintain optimal physical health. They educate patients on proper body mechanics, posture, and exercise to reduce the risk of injury.
- Musculoskeletal Health: From joint problems to muscle strains, physiotherapists specialize in treating musculoskeletal conditions. They employ a wide range of techniques to improve joint mobility and muscle strength.
- Neurological Rehabilitation: For individuals with neurological disorders like stroke, spinal cord injuries, or multiple sclerosis, physiotherapists play a vital role in restoring function and improving independence.
- Cardiovascular Health: Physiotherapists are involved in cardiac rehabilitation programs, helping patients recover after heart surgery or manage heart conditions through exercise and lifestyle changes.
Understanding Arthritis:
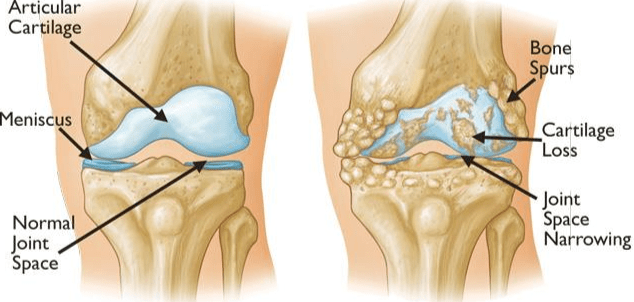
Arthritis is a broad term encompassing over 100 different types of joint-related conditions that affect people of all ages. The most common forms of arthritis include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and juvenile arthritis. Despite their differences, these conditions often share symptoms like joint pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
Types of Arthritis:
- Osteoarthritis (OA): The most common form, often associated with aging and wear-and-tear on joints. It primarily affects the joints in the hands, knees, hips, and spine.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): An autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the synovium (also called the synovial membrane) is a specialized connective soft-tissue membrane that lines the inner surface of synovial joint capsules. It is chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and, if left untreated, joint damage and deformities. Unlike osteoarthritis, in this immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissues.
- Juvenile Arthritis (JA): Juvenile arthritis refers to a group of autoimmune disorders that affect children and adolescents, leading to joint inflammation, pain, and swelling. Unlike arthritis in adults, juvenile arthritis occurs in individuals aged 16 or younger.
- Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS): A type of arthritis and a chronic inflammatory condition that primarily affects the spine and sacroiliac joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and potentially causing the vertebrae to fuse together over time. This condition falls under the category of spondyloarthritis and often begins in early adulthood.
- Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA): Psoriatic arthritis is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects individuals who have psoriasis, a skin disorder characterized by red, scaly patches on the skin.
- Gout: It is a form of arthritis characterized by sudden and severe attacks of pain, redness, and swelling in the joints, often affecting the big toe. These attacks are the result of the crystallization of uric acid in the joints.
Causes of Arthritis:
- Osteoarthritis: Resulting from the breakdown of joint cartilage over time.
- Genetics- A family history of OA may predispose individuals to the condition.
- Joint injury- Previous joint injuries or trauma can increase the likelihood of OA in affected joints.
- Obesity- Excess body weight places additional stress on weight-bearing joints, such as knees and hips.
- Joint Overuse- Repetitive joint use in sports, occupation, or daily activities can contribute to OA.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune response that attacks the synovium.
- Genetics- Family history of RA may increase the risk of developing the disease.
- Environmental factors- Certain environmental factors, such as infections, smoking, and hormonal changes, may trigger or exacerbate RA in genetically predisposed individuals.
- Juvenile Arthritis: Mostly idiopathic, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors.
- Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS): The exact cause of ankylosing spondylitis is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. A specific genetic marker called HLA-B27 is strongly associated with AS.
- Psoriatic Arthritis: The exact cause of PsA is not fully understood. Linked to both genetic and immune system factors.
- Gout: It is primarily caused by build-up of uric acid in the bloodstream.
- Diet- Consuming foods high in purines, such as red meat, seafood, and alcohol, can lead to increased uric acid production.
- Genetics- A family history of gout may increase the risk of developing the condition.
- Medical Conditions- Certain medical conditions like kidney disease, high blood pressure, and diabetes can contribute to gout.
- Medications- Some medications, such as diuretics, can elevate uric acid levels.
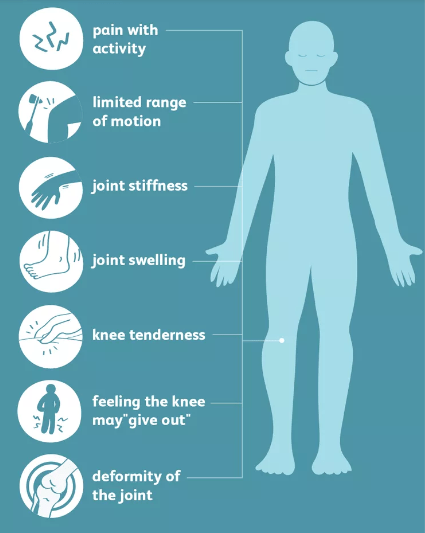
Signs and Symptoms:
- Joint Pain: Persistent discomfort in one or more joints.
- Joint Stiffness: Reduced range of motion and flexibility in affected joints.
- Swelling: Inflammation and swelling around the joint.
- Redness and Warmth: Affected joints may become warm and red to the touch.
- Fatigue: Generalized tiredness, often due to pain and inflammation.
- Morning Stiffness: Joints are stiffer in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
- Reduced Mobility: Difficulty in performing daily tasks due to joint limitations.
- Joint Crepitus: A crackling or grating sensation when joint is moved.
- Bony Enlargements: Formation of bony growths (osteophytes) around the joint.
- Fever: In the case of juvenile arthritis (JA), high fever spikes can occur along with rash and other systemic symptoms.
- Growth Problems: In some cases, JA can affect a child’s growth.
- Chronic Back Pain and Spinal Fusion: In AS there is persistent pain and stiffness in the lower back and buttocks, often worse in the morning or after menstruation of inactivity. Over time, AS can lead to the fusion of the vertebrae, causing reduction in spinal flexibility and mobility.
- Enthesitis: Inflammation where ligaments and tendons attach to bones, leading to pain and swelling.
- Skin and Nail Changes: Psoriasis skin lesions, characterized by red, scaly patches, are often present and also can cause changes in the nails, including pitting, thickening, or separation from the nail bed.
- Dactylitis: In psoriatic arthritis there is swelling of an entire finger or toe, giving it a “sausage-like” appearance.
Celebrating World Physiotherapy Day 2023:
- Creating Awareness: On this day, physiotherapy organizations worldwide engage in awareness campaigns, emphasizing the importance of physiotherapy in managing arthritis.
- Education: Physiotherapy clinics and institutions often host seminars, workshops, and webinars to educate the public about arthritis management.
- Empowering Patients: World Physiotherapy Day encourages individuals with arthritis to seek the support and guidance of physiotherapists, empowering them to take control of their condition and improve their quality of life.
- Community Outreach: Many physiotherapy professionals actively engage with local communities, offering free consultations, screenings, and exercise classes to individuals with arthritis.
How B Jain Pharmaceuticals Celebrating World Physiotherapy Day:
B Jain Pharmaceuticals celebrating World Physiotherapy Day by offering you B Jain OMEO Arthritis (Medicated Syrup), OMEO Arthro-Relief Drops, and OMEO Rheum-Ease Oil. This initiative can potentially benefit individuals who require physiotherapy and related treatments to manage various health conditions. It highlights the importance of a holistic approach to healthcare, combining both physiotherapy and medication when necessary. To Buy Homeopathic Medicines Online.
Conclusion:
World Physiotherapy Day serves as reminder that physiotherapists are healthcare heroes who contribute significantly to enhancing the physical and emotional well-being of individuals worldwide. Whether you are recovering from an injury, managing a chronic condition, or simply striving to maintain a healthy, active lifestyle, it is the collaborative efforts between pharmaceuticals companies like B Jain and healthcare practitioners to enhance patient care.

Dr Simranjit Kaur
Dr Simranjit Kaur is a highly accomplished medical professional with a BHMS degree from BVDU Pune and additional qualifications including CGO and MBA(Hospital Administration). With a passion for paediatric care, Dr. Simranjit pursed a fellowship in paediatrics, honing expertise in the specialized field. Currently Research Officer at BJain Pharmaceuticals.