Back pain is defined as the physical discomfort in any region of the spine or back and can range from mild to severe and disabling. There can be various causes of back pain such as injury, strain, sprain, sudden movements, bad posture, structural abnormalities and sometimes it can be due to underlying health conditions such as kidney disorders.
Types of Back Pain, its Risk factors, Diagnostic Methods, and the difference between Spondylitis and Spondylosis.

Risk factors for Tendency to Back Pain include:
- Lack of exercise
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Bad posture
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Occupational Injuries
- Genetic Factors
- Pregnancy
- Poor nutrition
- Old Age
- Medical Conditions such as Arthritis, Osteoporosis, etc.
Diagnostic Methods for Back Pain:
- X rays: They can help detect injuries or abnormal bony growths that can cause back pain.
- MRI/ CT Scans: These can detect disc herniation or troubles with tissues, nerves, tendons, vessels and muscles.
- Bone Scans: These are done using a technique called nuclear imaging and can detect conditions such as bone cancer and compound fractures.
- Electromyography: EMG is a technique used to measure the electrical impulses of the nerves in response to muscles. It helps detect nerve compressions and injuries as a cause for pain.
- Blood Tests: Tests such as CBC, Sed Rate and C-Reactive Protein can be used to test for infections and inflammation. HLA B27 is a genetic marker for Ankylosing spondylitis and Rheumatoid arthritis which may be suggested in cases of chronic back ache.
Types of Back Pain:
On the basis of duration of the pain, there are mainly 3 categories of Back Pain:
- Acute: Acute back pain is short term lasting from 1 day to 4 weeks. It can arise due to specific events such as injury, stretch, sprain, over lifting or from a fall. It requires management for pain and swelling and can sometimes even require a visit to the doctor based on intensity and cause of pain.
- Subacute: This is when pain can last between 4 weeks to 12 weeks and usually requires a doctor visit and diagnostic tests to find the underlying cause.
- Chronic: It is pain that lasts for more than 12 weeks and can be dull aching or sharp and sudden. It can also mean flare-ups of pain at regular or irregular intervals. Lifestyle management and assistive techniques are often required along with medical care for such pains.
Spondylitis v/s Spondylosis
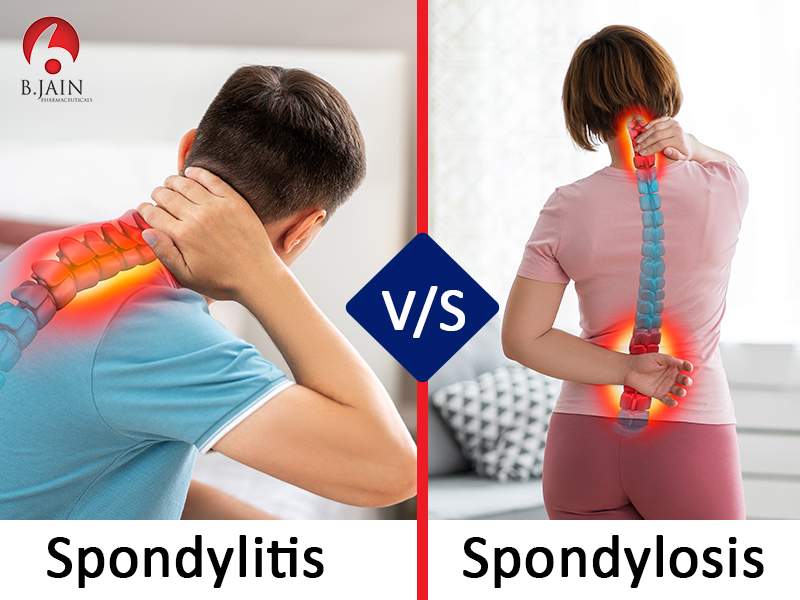

While both Spondylitis and Spondylosis present as pain in the back and are conditions involving the joints in the spine, there are various differences between the two which are highlighted below:
| Factor | Spondylitis | Spondylosis |
| Cause | It occurs as a result of an inflammatory condition causing arthritis. | It occurs as a result of degeneration of discs and joints of the spine due to general wear and tear. |
| Pathology | Bones grow towards each other resulting in fusion and limitation in mobility. | Bone pieces grow to provide stability in areas of degeneration giving rise to bone spurs that cause pain and stiffness. |
| Symptoms | Symptoms include: • Stiffness and soreness • Pain • Worse after rest • Tingling in extremities • Disturbance in sleep from pain | Symptoms include: • Neck pain and stiffness extending to arms and shoulders • Headaches • Balance issues • Numbness • Weakness in arms and legs. |
| Treatment | Treatment includes analgesics for pain, anti-inflammatory medicines, exercise to improve mobility, surgery as last resort. | Anti-inflammatory medicines, exercise, surgery as last resort. |
Omeo Spondyheal Drops
B Jain’s Omeo Spondyheal Drops is a specialty product and is suited for pain and stiffness of back concentrated in the cervical and lumbar-sacral region.
Indications:
- Pain in back
- Stiffness in the back
- Difficulty in movement
Key Ingredients:
Indications:
- Neuralgic pains relieved by pressure.
- Cramping, twitching and shortening of muscles.
- Pain as if bruised and as if clamped by an iron band.
- Contraction of limbs as if drawn together.
- Pain better by pressure, heat and by bending double.
Indications:
- Complaints from straining especially the flexor tendons.
- Pain in body as if bruised.
- Sprains and lameness after them.
- Feeling of injured bones.
- Weakness of legs on getting up.
- Pain in back better by pressure and by lying on the back, worse in the morning before getting up from the bed.
Indications:
- Injuries to nerves, crush injuries.
- Excessive painfulness, unbearable.
- Spasms after injuries.
- Nerve involvement with tingling, burning and numbness.
- Pain in nape of neck and pressure over sacrum.
Indications:
- Rheumatism that begins in the feet and goes upwards.
- Lack of heat in the body but heat of bed is intolerable.
- Wounded parts feel cold.
- Gouty pains with swollen, hot and pale joints.
- Better from cold and by putting feet in cold water, worse at night and from heat of the bed.
Indications:
- Spasms, cramps, convulsions, contractions.
- Complaints begin in the left side.
- Periodic complaints, occur in groups.
- Jerking and twitching of muscles.
- Coldness and cramps in hands.
- Complaints better from sweat and from drinking cold water.
Indications:
- Rheumatic complaints brought on by dampness and cold.
- Pain better by movement.
- Pain in the small of back, from stooping.
- Rheumatism and diarrhea alternate.
- Rheumatic complaints after suppressed skin eruptions.
Indications:
- Difficult gait, trembling, loss of strength while walking, stiffness.
- Pain between shoulders.
- Complaints after injury to spine.
- Dull aching in lumbar and sacral region.
- Complaints better by motion and by pressure.
Here are a few helpful tips for the General Management of Back Pain:
- Hot fomentation
- Physiotherapy
- Supportive gear
- Assistive equipment
Read More our blog about – Medicated Syrup for Cough Relief in Homoeopathy