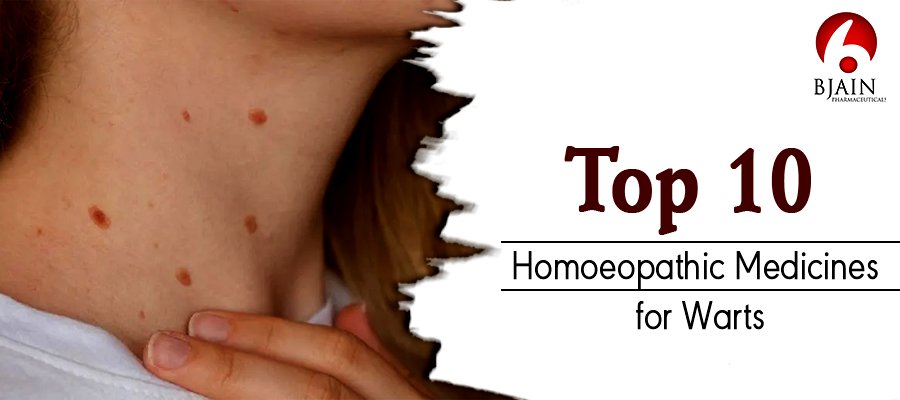
Specific types of the human papillomavirus cause skin growths known as warts. You can find several varieties, including flat, typical, and plantar warts. Although warts might be difficult to remove, there are several treatment methods available.
What are Warts?
Warts on the outer layer of skin and mucosa (such as in your mouth) are benign, or noncancerous, development that can appear. HPV, the human papillomavirus, brings on warts. Although there are more than 100 HPV variants (kinds), only a small number of these strains can result in warts on specific body regions.
Although they are usually not harmful, warts can cause irritation and sometimes discomfort.
What are the types of Warts?
Healthcare professionals classify warts based on their appearance, the HPV variant (kind) that produces them, and the organ components they impact:
Common warts: They generally appear on the areas around the hands. They can have black flecks that mimic seeds and are normally firm masses. The black flecks are dead blood vessels that have been coated. Their size ranges from a tiny seed to a pinhead.
Plantar warts: They often form on the bottom of your feet. They may have black patches and tend to be flattened or inward-growing. They might develop to be large and painful when you walk or stand.
Mosaic warts: These skin growths resemble pinhead-sized white pimples. Usually, they develop beneath your toes or on the soles of your feet. However, they can proliferate and include more of your foot. Compared to plantar warts, they are flat and rarely cause pain when walking.
Flat warts: You might get these warts at any location on your body. Compared with other types of warts, they are smoother and smaller and often form clusters of between 20 and 100 at one point.
Filiform warts: These growths resemble protruding, lengthy threads. They are most commonly seen around your mouth, eyes, and nose on your face.
Genital warts: They afflict your rectum and genitalia. It’s a skin-to-skin contact-transmitted, and sexually transmitted infection (STI). Tiny, rigid nodules with uneven surfaces are known as genital warts.
Who is inclined to get warts?
While warts may afflict anybody, certain individuals are more prone to developing them than others.
- Age: Young people, especially kids, are more inclined to get warts.
- Ethnic origin: White people are more likely to get warts than black or Asian people.
- Immunity: People with impaired immune systems may be more susceptible to warts than others.
How can we prevent warts?
If you currently have a wart, some techniques can avoid the spread to various areas of your skin. Consider these basic instructions:
- Wash your hands frequently, particularly if you’ve come in contact with a person who has warts.
- Never pick on your warts.
- Wrap the warts with a covering.
- Keep your fingers and toes dry.
- When visiting a community bathing facility, wear bath shoes (slippers).
What are the homeopathic medicines for the warts?
- Thuja occidentalis: The most often used homeopathic medicine for various types of warts. If no alternative remedy is evident, consider Thuja. This is especially true for solitary, ragged warts that are pungent or bleed readily, as well as mosaic types of warts on the sole.
External application of Thuja ointment on your warts can help them reduce significantly. Always consult to a homeopathic physician for advice.
- Dulcamara: Flat warts appear on the inner surfaces of your arms and face, as do light brown to black seborrheic warts on the back. Suitable for rheumatic conditions that worsen in cold, humid conditions or dampness.
- Ferrum picricum: Tiny pointy warts develop in huge groupings. Also effective in some instances of smooth or plane warts with uneven boundaries that appear on the face, neck region, wrists, arms, and knees.
- Graphites: Particularly in periungual or corn-shaped warts on the palms and soles of the feet, which can look yellow. This is not merely a homeopathic cure for warts, but it also treats numerous other skin problems, such as eczema.
- Nitricum acidum: This homeopathic medicine is suggested for big, fissured, or golden-yellow that itch, sting, or bleed when washed. This medicine is also recommended for persons who are concerned about their health and fear about cancer. Often beneficial for warts with a hard wall around a core dent, such as the more frequent plantar wart.
- Antimonium crudum: This medicine is best suited for rough and smooth warts that form in clusters. These types of warts are commonly encountered on the soles and hands.
- Causticum: This cure is for old, huge warts that occur on one’s face (nose), the nail beds, as well as on the fingertips. These warts are firm, unpleasant, and bleed quickly.
- Calcarea carbonica: This medicine is effective for addressing circular, firm warts on the neck area that form on their own.
- Sepia officinalis: It is indicated for flattened warts in women, especially during hormonal shifts like maternity or menopause. These warts can be dark brown or black in appearance and develop on your neck, face, or torso.
- Sulphur: It is recommended for plain warts that feel itchy, burning, or cause a sense of heat. These warts can be scaly, crusty, or inflammatory, and they tend to aggravate at night or in hot weather.
Conclusion:
Homeopathic medicines for warts are a gentle, safe method that focuses on particular signs and general health to support the body’s repair mechanisms. Homeopathy uses diluted herbal extracts to decrease wart formation and avoid relapse without the adverse effects related to traditional therapies. As with any kind of medical care, it is essential to speak with a proficient homeopathic physician to establish a customized course of action that suits your requirements.

Dr Aditi
Dr Aditi (BHMS) from NHMC Delhi, HMO ( Chandigarh Administration), Ex- SRF ( CCRH ), currently doing a research study of effect of Homoeopathic medicines in Mother and Child Health care in Chandigarh.