Introduction:
World Alzheimer’s Day, observed on September 21st each year, provides an opportunity to raise awareness about Alzheimer’s disease and related forms of dementia. It is a day dedicated to understanding the challenges faced by individuals living with dementia and their families, as well as recognizing the importance of research and support in the fight against this debilitating condition. The Theme of World Alzheimer’s Day 2023 is “Never too early never too late”. In this blog, we will delve into the significance of World Alzheimer’s Day and explore the global efforts to address this growing health crisis.
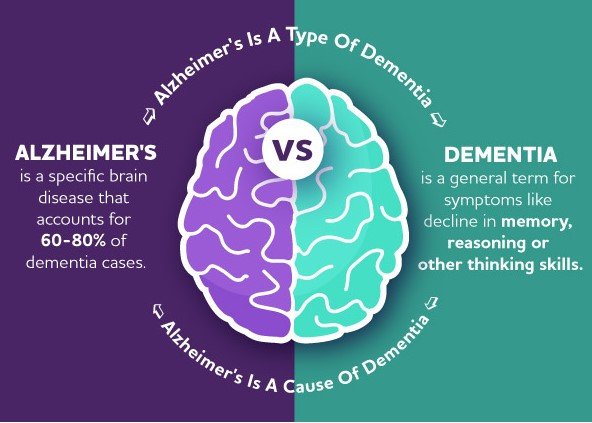
What is Dementia?
Dementia is a broad term that refers to a set of symptoms characterized by a decline in cognitive function, including memory, thinking, reasoning, and the ability to perform everyday activities. Dementia is typically progressive, meaning symptoms worsen over time. Early stages may involve mild cognitive impairment, while later stages can severely impact a person’s independence and ability to function.
Types of Dementia:
- Alzheimer’s disease: The most prevalent cause of dementia, characterized by abnormal protein deposits in the brain leading to cognitive decline.
- Vascular Dementia: Caused by reduced blood flow to the brain due to strokes or other vascular issues, resulting in cognitive impairments.
- Lewy Body Dementia: It involves the accumulation of abnormal protein deposits called Lewy bodies in the brain, leading to cognitive and motor symptoms.
- Frontotemporal Dementia: A group of disorders primarily affecting the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain, leading to changes in behaviour and personality.
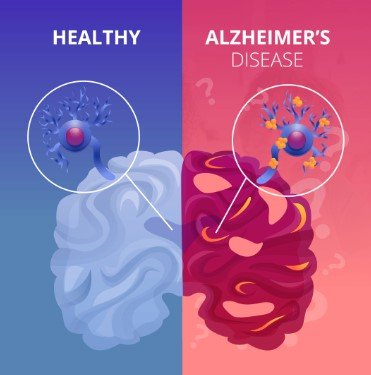
What is Alzheimer’s disease?
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive and irreversible neurological disorder that primarily affects cognitive function, memory, thinking, and behaviour. It is the most common cause of dementia among older adults, accounting for a significant majority of dementia cases.
Here are key characteristics and aspects of Alzheimer’s disease:
- Cognitive Decline: Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by a gradual decline in cognitive abilities. These includes memory loss, difficulty with problem-solving and decision-making, impaired language skills, and challenges in performing everyday tasks.
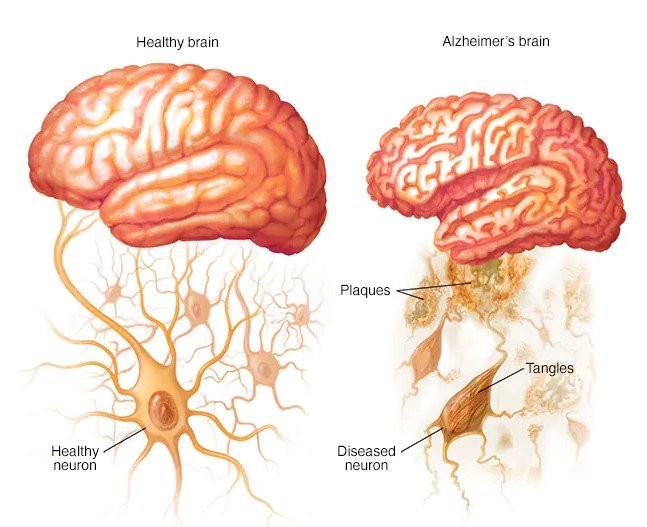
- Pathological Changes: The brain of an individual with Alzheimer’s undergoes physical changes, including the accumulation of two abnormal protein deposits: beta-amyloid plaques and tau tangles. These deposits interfere with the normal functioning of brain cells, leading to their damage and eventual death.
- Stages of Progression: It is typically progresses through several stages:
- Early Stage: Mild memory loss and subtle cognitive changes.
- Middle Stages: More noticeable memory and cognitive deficits, mood swings, and difficulty with daily tasks.
- Late Stage: Severe cognitive decline, loss of communication skills, inability to recognize loved ones, and the need for full-time care.
4. Impact on Families: Alzheimer’s disease not only affects the individual diagnosed but also has a profound impact on their families and caregivers. Caregiving can be emotionally and physically demanding, and support services and resources are available to help families navigate the challenges.
5. Ongoing Research: Its research continues to explore potential causes, risk factors, prevention strategies, and treatment options. The goal is to find effective ways to slow or halt the progression of the disease and, ultimately, to find a cure.
Risk Factors for Alzheimer’s disease:
- Age: Advancing age is the most significant risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. The risk increases as individuals get older, with most cases occurring in people over the age of 65.
- Family History: A family history of Alzheimer’s disease may increase an individual’s risk, especially if a first-degree relative (parent or sibling) has been diagnosed.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop Alzheimer’s than men, primarily due to their longer life expectancy.
- Cardiovascular Health: Risk factors for heart disease, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes, are also risk factors for Alzheimer. Maintaining good cardiovascular health may reduce the risk.
- Lifestyle Factors: Unhealthy lifestyle choices, such as a sedentary lifestyle, a poor diet, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption, may contribute to an increased risk.
Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease:
Diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease involves a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional, typically a neurologist or geriatrician. The diagnosis process may include:
- Medical History: Gathering information about the individual’s medical history, symptoms, and any family history of dementia.
- Physical and Neurological Exams: Conducting a physical examination and neurological assessment to identify any physical or cognitive changes.
- Cognitive Assessments: Administering cognitive tests and assessments to evaluate memory, problem-solving abilities, language skills, and other cognitive functions.
- Blood Tests: Checking blood samples to rule out other potential causes of cognitive impairment, such as vitamin deficiencies, thyroid problems, or infections.
- Neuroimaging: Using brain imaging techniques like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans to identify structural brain changes associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
- Biomarker Testing: Emerging biomarker tests, including cerebrospinal fluid analysis or positron emission tomography (PET) scans, may be used to detect specific protein abnormalities in the brain, such as beta-amyloid and tau, which are characteristic of Alzheimer’s disease.
- Functional Assessment: Evaluating the individual’s ability to perform daily tasks and activities of daily living (ADLs).
- Rule-Out Tests: Excluding other potential causes of cognitive decline, such as vascular dementia or frontotemporal dementia.
Best Homoeopathic Medicines for Individuals with Alzheimer’s disease or Cognitive Decline:
- Ginkgo Biloba: B Jain Ginkgo biloba is a popular herbal remedy that has been explored for its potential to improve cognitive functions in some individuals.
- Lycopodium Clavatum: Wonderful remedy for cognitive issues and memory problems. Afraid to be alone. Constant fear of breaking down under stress. Weak memory, confused thoughts; spells or writes wrong words and syllables. Failing brain power. Cannot bear to see anything new. Cannot read what he writes. Sadness in the morning on awaking.
- Baryta Carbonica: This medicine specially indicated in infancy and old age. Diseases of old men when degenerative changes begin, cardiac, vascular and cerebral, who have a hypertrophied prostate or indurated testes, are very sensitive to cold, have offensive foot sweats and are very weak and weary, must sit, lie down or lean on something. Loss of memory, mental weakness. Loses confidence in himself. Senile dementia, with confusion, bashful, aversion to strangers. Childish; grief over trifles.
- Phosphoric Acid: The common acid “debility” is very marked in this remedy, producing a nervous exhaustion. Mental debility first; later physical. Impaired memory, cannot collect his thoughts to find the right word. Effects of grief and mental shock. Delirium with great stupefaction. Difficult comprehension. To buy Homeopathic medicines online.
World Alzheimer’s Day: A Call to Action:
- Raising Awareness: It serves as a global platform to raise awareness about the impact of dementia on individuals, families, and communities. By shedding light on the challenges faced by those living with dementia, we can reduce stigma and foster empathy and understanding.
- Advocating for Research: Research into Alzheimer’s disease is crucial for understanding its causes, risk factors, and potential treatments. This day encourages governments, healthcare organizations, and the public to support and fund research efforts aimed at finding a cure or effective treatments.
- Supporting Caregivers: Alzheimer’s disease places a significant burden on caregivers who provide care and support to individuals with dementia. Recognizing and supporting the needs of caregivers is an essential aspect of world Alzheimer’s Day.
- Promoting Early Detection: Early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease allows for better management of symptoms and access to appropriate support and services. World Alzheimer’s Day encourages individuals and healthcare providers to be vigilant for signs of dementia and seek timely diagnosis.
- Enhancing Dementia Friendly Communities: Creating dementia-friendly communities involves fostering environments where individuals with dementia can live with dignity and participate in society. This includes initiatives to improve accessibility, provide social engagement opportunities, and ensure safety for people with dementia.
- Global Collaboration: Alzheimer’s is a global challenge that requires international cooperation. World Alzheimer’s Day encourages countries and organizations to collaborate in addressing the impact of dementia on a global scale.
Conclusion:
World Alzheimer’s Day serves as a reminder of the urgent need to address Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. As the global population continues to age, the prevalence of dementia is expected to rise. However, with increased awareness, research, support, and collaboration, we can strive for a world where individuals living with Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias receive the care and respect they deserve. Together, we can work towards a future where Alzheimer is better understood, prevented, and ultimately cured. On this World Alzheimer’s Day, let us remember, empathize, and resolve to make a difference in the lives of those affected by dementia.
Please visit our previous blog – World Patient Safety Day 2023: Engaging Patients for Patient Safety

Dr Simranjit Kaur
Dr Simranjit Kaur is a highly accomplished medical professional with a BHMS degree from BVDU Pune and additional qualifications including CGO and MBA(Hospital Administration). With a passion for paediatric care, Dr. Simranjit pursed a fellowship in paediatrics, honing expertise in the specialized field. Currently Research Officer at BJain Pharmaceuticals.