Introduction:
Every year on September 29th, people across the globe observe World Heart Day. This important day serves as a reminder of the significance of heart health and the global battle against cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). Established by the world heart Federation, world heart day encourages individuals, communities, and healthcare professionals to take action and promote heart-healthy lifestyles. In this blog, we’ll explore the importance of heart health, the global impact of cardiovascular diseases, and practical steps we can take to keep our heart in top shape.
Understanding Importance of Heart Health:
Your heart is a remarkable organ responsible for pumping blood throughout your body, supplying oxygen and nutrients to your cells. Maintaining heart health is vital because cardiovascular diseases, including heart disease and stroke, are among the leading causes of death worldwide.
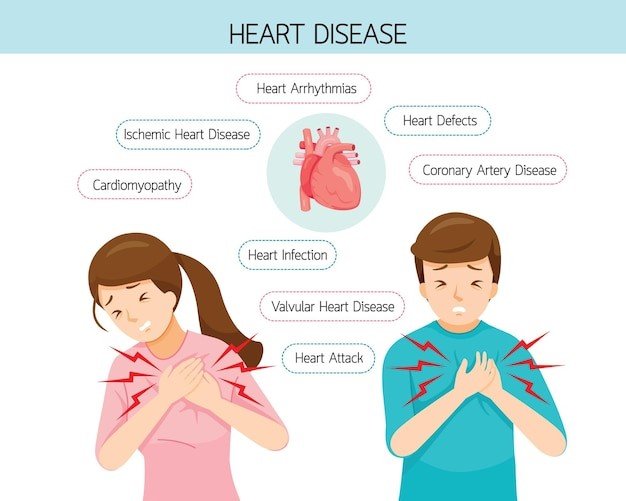
Types of Heart Diseases: Heart diseases, also known as cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), encompass a range of conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels. These conditions can lead to various symptoms and complications.
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): This is the most common type of heart disease. CAD occurs when the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle, become narrow or blocked due to the buildup of plaque (atherosclerosis).
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): It is a condition where the force of blood against the artery walls is consistently too high. Over time, it can damage blood vessels, the heart, and other organs, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems.
- Heart Failure: It occurs when the heart cannot pump blood effectively, leading to a reduced supply of oxygen and nutrients to the body’s tissues. It can result from conditions like CAD, hypertension, or cardiomyopathy.
- Arrhythmias: Arrhythmias are irregular heart rhythms. They can range from harmless to life-threatening and may cause palpitations, dizziness, fainting, or chest discomfort. Atrial fibrillation is a common type of arrhythmia.
- Valvular Heart Disease: This involves problem with the heart’s valves, which control blood flow through the heart. Conditions like aortic stenosis (narrowing of the aortic valve) and mitral regurgitation (leaking of the mitral valve) are examples of valvular heart diseases.
- Cardiomyopathy: It is a disease of the heart muscle. It weakens the heart’s ability to pump blood and can result from various causes, including genetics, infections, or exposure to toxins.
- Congenital Heart Disease: These are heart conditions present at birth. They can involve structural defects in the heart or its blood vessels, such as atrial septal defects or tetralogy of Fallot.
- Pericardial Disease: This involves conditions affecting the pericardium, the sac surrounding the heart. Pericarditis is an example, which is inflammation of the pericardium.
- Rheumatic Heart Disease: This rare condition can result from untreated strep throat or scarlet fever. It can cause damage to heart valves.
- Cor Pulmonale: This type of heart disease occurs when the right side of the heart is affected due to lung conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or pulmonary hypertension.
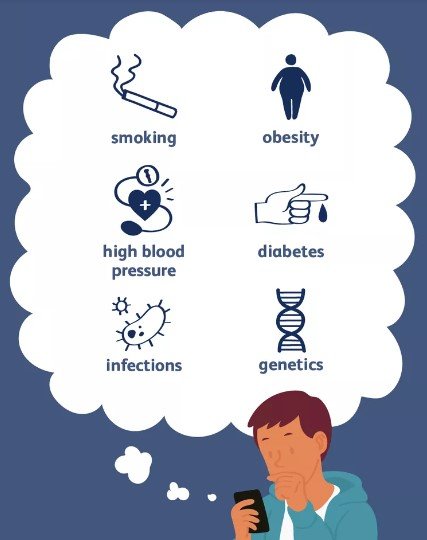
Common Causes of Heart Diseases:
- Atherosclerosis: This is the primary cause of coronary artery disease (CAD) and involves the buildup of plaque (cholesterol, fat, calcium, and other substances) on the inner walls of arteries. Over time, the plaque narrows the arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart.
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): Uncontrolled high blood pressure can damage the arteries, making them more susceptible to atherosclerosis. It also increases the workload on the heart, leading to heart strain.
- Smoking: It damages blood vessels and accelerates atherosclerosis.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, increasing the risk of heart disease.
- High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol are associated with an increased risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can contribute to various heart disease risk factors, including hypertension and diabetes.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of regular exercise is a risk factor for heart disease. Exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, control blood pressure, and improve heart health.
- Family History: A family history of heart disease can increase your risk due to shared genetic and lifestyle factors.
- Age: The risk of heart disease increases with age, particularly after the age of 65.
- Gender: Men are generally at a higher risk for heart disease than premenopausal women, although the risk for women increases after menopause.
Symptoms of Heart Diseases:
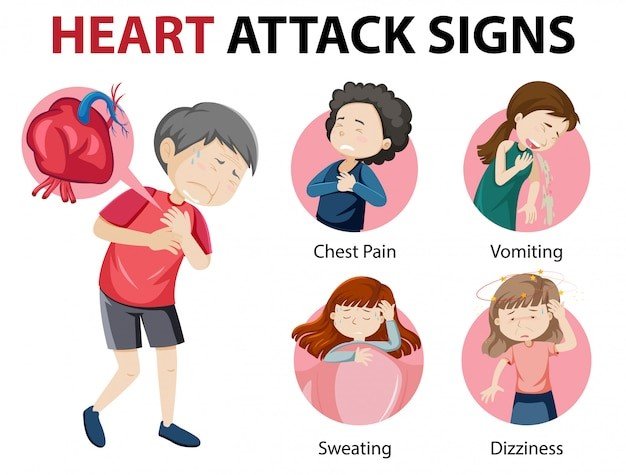
- Chest Pain or Discomfort (Angina): This is a common symptom of coronary artery disease. It may feel like pressure, tightness, or pain in the chest, which can radiate to the neck, jaw, shoulder, or arm.
- Shortness of Breath: This symptom can occur with exertion or at rest and may be due to heart failure, valve problems, or other heart conditions.
- Fatigue: Unexplained fatigue or weakness can be symptom of heart failure.
- Irregular Heartbeat (Arrhythmia): Arrhythmia can cause palpitations (awareness of the heartbeat), fluttering, racing, or a slow heartbeat.
- Swelling: Fluid retention can lead to swelling in the legs, ankles, abdomen, or other areas.
- Dizziness or Fainting: These symptoms may occur due to arrhythmias or inadequate blood flow to the brain.
- Cold Sweats: Clammy or cold sweats can accompany chest pain or other heart related discomfort.
- Nausea or Indigestion: Some people experience stomach discomfort, nausea, or vomiting during a heart attack.
- Pain that Radiates: Pain or discomfort that spreads from the chest to the arms, neck, jaw, or back can be a sign of heart trouble.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Heart Diseases:
- Healthy Eating:
- Balanced Diet: Consume a well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins (like fish and poultry), and low-fat dairy products.
- Limit Saturated and Trans Fats: Reduce your intake of saturated fats found in red meat, full-fat dairy products, and tropical oils.
- Control portions of meal.
2. Regular Exercise:
- Activities like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling are excellent choices.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can lower your risk of heart disease. If you are overweight, even losing a small amount of weight can be beneficial.
4. Manage Stress:
- Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or hobbies that help you relax.
- Seek support from friends, family, or a counselor if you are dealing with chronic stress.
5. Quit Smoking: Smoking is the major risk factor.
6. Monitor Your Blood Pressure:
- Regularly check your blood pressure, and if it’s elevated, work with your healthcare provider to manage it through lifestyle changes or medication.
7. Manage Diabetes:
- If you have diabetes, work with your healthcare team to keep your blood sugar levels under control.
8. Get Enough Sleep:
- Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Poor sleep can contribute to heart disease risk factors like obesity and hypertension.
9. Limit Salt Intake and Stay Hydrated:
- Reduce your sodium intake by avoiding high-salt processed foods and using herbs and spices for flavor instead of salt.
- Drink at least 12-15 glasses of water/day.
10. Limit alcohol intake.
The Global Impact of Cardiovascular Diseases:
Here are some global statistics highlighting the severity of the issue:
- CVDs are leading cause of death worldwide, responsible for over 17 million deaths each year.
- High blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and obesity are common risk factors for heart disease.
- Many heart-related risk factors are preventable through lifestyle changes.
Taking Action on World Heart Day:
- Know Your Numbers: Regularly monitor your blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar. Understanding your numbers is the first step in managing your heart health.
- Stay Active
- Eat Heart-Healthy: Make nutritious food choices, emphasizing fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Reduce your intake of processed foods and limit added sugars and salt.
- Quit Smoking: Seek support to quit smoking if you are a smoker. It’s never too late to quit, and your heart health will improve almost immediately.
- Raise Awareness: Spread the word about World Heart Day and the importance of heart health within your community. Encourage friends and prioritize their hearts.
Conclusion:
On World Heart Day, we reflect on the importance of heart health and the various approaches available to support and manage cardiovascular conditions. Among these approaches are homeopathic remedies offered by B Jain Pharmaceuticals, including “Gautteria Gaumeri for High Cholesterol levels,” “Omeo Cardio Plus provides strength to your heart,” “Omeo Be Pe Tone Drops for Hypertension,” “Omeo Uprise Be Pe Drops for Low Blood pressure.” On World Heart Day, we should acknowledge the significance of a holistic approach to heart health. This approach includes maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle, seeking guidance from qualified healthcare professionals, and considering complementary therapies like Homeopathy as part of an overall care plan.
Please visit our previous blog – World Rabies Day: All for One,One Health for All

Dr Simranjit Kaur
Dr Simranjit Kaur is a highly accomplished medical professional with a BHMS degree from BVDU Pune and additional qualifications including CGO and MBA(Hospital Administration). With a passion for paediatric care, Dr. Simranjit pursed a fellowship in paediatrics, honing expertise in the specialized field. Currently Research Officer at BJain Pharmaceuticals.