Introduction:
World Suicide Prevention Day, observed on the 10th of September each year, is a global initiative aimed at raising awareness about the profound issue of suicide and promoting actions to prevent it. This day serves as a reminder that we can make a difference in the lives of those struggling with suicidal thoughts, and that by working together, we can create hope through action. In this blog, we will explore the significance of World Suicide Prevention Day, it’s theme of “Creating Hope through Action,” and practical steps we can take to make a positive impact.
Understanding the Importance:
Suicide is a complex and devastating global issue. It claims the lives of over 800,000 people annually, leaving countless others deeply affected by the loss of their loved ones. The pain and stigma surrounding suicide often prevent individuals from seeking help, making it crucial to raise awareness and provide support.
The Theme: “Creating Hope through Action”
This theme for 2023, emphasizes that each one of us can play a role in preventing suicide. This theme underscores the idea that hope is not just an abstract concept but something tangible that can be fostered through our actions.
Depression and Suicidal Thoughts:
One of the most concerning aspects of depression is its potential link to suicidal thoughts and behaviours. It is crucial to recognize that not everyone with depression experiences suicidal thoughts, but for those who do, it is a serious and urgent matter.
What is Depression???
Depression is a complex and multifaceted mental health disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It’s more than just feeling sad; it’s persistent and pervasive feeling of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest or pleasure in activities that were once enjoyable.
Types of Depression:
1. Major Depressive Disorder (MDD):
- It is commonly referred to as depression, is a clinical diagnosis for a severe form of depression.
- It involves a persistent and pervasive low mood, loss of interest or pleasure in most activities, and a range of other symptoms that significantly affect a person’s daily life.
- Symptoms often interfere with daily life and can last for weeks, months, or longer.
2. Persistent Depressive Disorder (Dysthymia):
- It is formerly known as Dysthymia, is a chronic form of depression characterized by a prolonged and persistent low mood that lasts for at least two years in adults and one year in children and adolescents.
- Symptoms may be less severe than MDD but are long-lasting and can lead to functional impairment.
3. Bipolar Disorder (formerly known as Manic Depression):
- Characterized by mood swings between periods of intense euphoria (mania) and severe depression.
- Bipolar I involves full-blown mania and major depressive episodes, while Bipolar II involves hypomania (less severe mania) and major depressive episodes.
4. Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD):
- It is a type of depression that occurs at a specific time of year, typically during the fall and winter months when there is less natural sunlight.
- Symptoms include low energy, increased sleep, and weight gain.
- Key characteristics include: Seasonal pattern, depressive symptoms, hypersensitivity to light, and remission in spring or summer.
5. Postpartum Depression (PPD):
- Affects some women after giving birth, with symptoms such as sadness, fatigue, and irritability.
- Hormonal changes, stress, and sleep disturbances can contribute to PPD.
6. Psychotic Depression:
- Combines severe depression with symptoms of psychosis, such as delusions (false beliefs) and hallucinations (false perceptions).
- Individuals with psychotic depression may be at higher risk of self-harm or suicide.
7. Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD):
- A severe form of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) characterized by mood disturbances, irritability, and physical symptoms in the days leading up to menstruation.
8. Atypical Depression:
- Features symptoms that differ from typical depression, including increased appetite, weight gain, excessive sleep, and a mood that temporarily improves in response to positive events.
9. Situational or Reactive Depression:
- Triggered by specific life events or stressors, such as the loss of a loved one, a divorce, or a major change in circumstances.
- Symptoms may resolve when the situation improves or with time.
10. Subsyndromal Depression:
- Also known as “sub threshold depression” or “minor depression”.
- Features some depressive symptoms but does not meet the criteria for a full-blown depressive disorder.
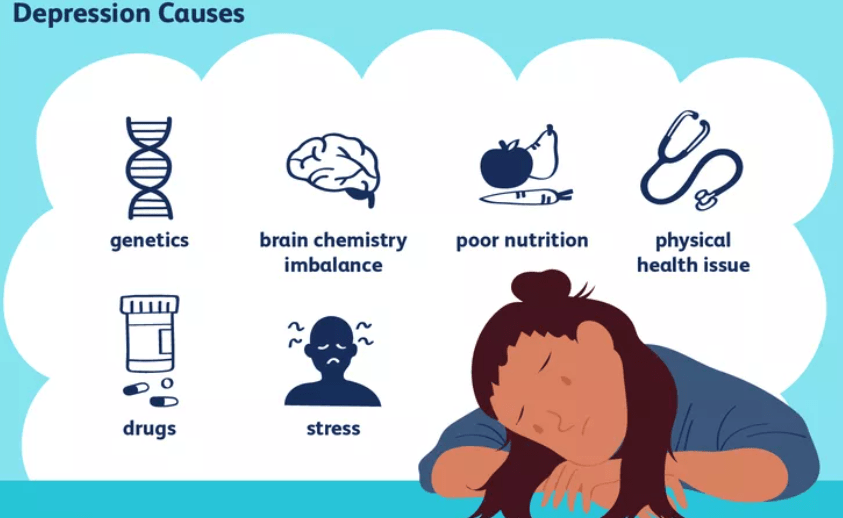
Causes of Depression:
- Biological Factors:
- Genetics- A family history of depression can increase the risk.
- Brain Chemistry- Imbalances in neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and norepinephrine, play a role in mood regulation.
- Hormonal Changes- Hormonal fluctuations, such as those during pregnancy or menopause, can trigger depression.
Psychological Factors:
- Trauma- Post traumatic events, abuse, or loss can contribute to depression.
- Stress- Chronic stressors, such as work-related stress or financial difficulties, can be a factor.
- Negative Thought Patterns- Persistent negative thinking and self-criticism can lead to depression.
Medical Conditions:
- Certain medical conditions such as chronic illness, chronic pain, or thyroid disorders, can increase the risk of depression.
- Medications- Some medications, including certain antihypertensives and corticosteroids, may have depressive side effects.
Substance Abuse:
- Alcohol and drug abuse can both lead to and exacerbate depression.
Environmental Factors:
- Isolation- Social isolation or lack of a strong support system can contribute to depression.
- Childhood Adversity- Adverse childhood experiences such as neglect or abuse, can increase the likelihood of depression in adulthood.
Common Symptoms of Depression:
Depression symptoms can vary in severity and duration, but they generally include:
- Persistent Sadness: Feeling persistently sad, empty, or hopeless for most of the day, nearly every day.
- Loss of Interest: losing interest or pleasure in activities once enjoyed, including hobbies, social interactions, and sex.
- Fatigue: A persistent feeling of fatigue, low energy, and physical sluggishness.
- Sleep Disturbances: Changes in sleep patterns, such as insomnia (difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep) or hypersomnia (excessive sleep).
- Appetite and Weight Changes: Significant changes in appetite and weight, either overeating or loss of appetite resulting in weight gain or weight loss.
- Difficulty Concentrating: Trouble with concentration, memory and decision making.
- Feeling of Worthlessness: Feelings of worthlessness or excessive guilt, often disproportionate to the situation.
- Irritability: Increased irritability, restlessness, or agitation.
- Physical Symptoms: Unexplained physical symptoms, such as headaches or digestive problems, without a clear medical cause.
- Suicidal Thoughts: Thoughts of death or suicide, or suicide attempts. This is a severe symptom that requires immediate attention.
Ways to Create Hope through Action:
- Break the Silence: One of the most significant barriers to seeking help is the stigma associated with mental health issues. By starting open and honest conversations about mental health, we can reduce this stigma and encourage those in need to speak up.
- Learn the Warning Signs: Educate yourself about the warning signs of suicide, such as withdrawal from friends and family, extreme mood swings, or giving away possessions. Recognizing these signs can be the first step in helping someone at risk.
- Support Networks: Strengthen support networks for individuals at risk. Let them know you care and are there to listen without judgement.
- Promote Professional Help: Encourage individuals to seek professional help, whether it’s therapy, counselling, or psychiatric assistance. Make information about available resources easily accessible.
- Advocate for Policy Change: Support policies that prioritize mental health services and suicide prevention. Advocate for increased funding and awareness campaigns in your community.
- Share Stories of Hope: Share stories of individuals who have overcome suicidal thoughts or experiences. These stories can inspire hope and show that recovery is possible.
- Self-Care: Remember that you can only help others if you take care of yourself first. Self-care is essential for maintaining the mental and emotional strength needed to support others.
8 Best Homeopathic Medicines for Depression and Suicidal Thoughts:
- Aurum Metallicum: This remedy is often used for individuals with deep sadness, feeling of worthlessness, and a sense of hopelessness, which may lead to thoughts of suicide.
- Natrum Muriaticum: People who benefit from this remedy often have suppressed emotions, grief, and isolation. They may experience sadness and tearfulness, which can lead to depression.
- Ignatia Amara: Suicidal thoughts arising from grief, disappointment, or emotional shocks may be addressed with ignatia. Individuals may have mood swings, sigh frequently, and have difficulty expressing their emotions.
- Staphysagria: This remedy may be indicated in cases of suppressed anger, humiliation, or emotional wounds that lead to depression and thoughts of self-harm.
- Lachesis Mutus: Lachesis is considered when individuals feel trapped or suffocated in their lives, leading to depression and potentially dangerous thoughts. They may have a fear of being confined or betrayed.
- Stramonium: In cases where there are violent or aggressive thoughts accompanying depression, stramonium may be considered. This remedy is often used for individuals with extreme fear, restlessness and agitation.
- Carcinosinum: For individuals with a family history of cancer or deep emotional scars, Carcinosinum may be indicated. It is used when depression is related to unresolved emotional issues.
- Aurum Arsenicum: This remedy may be beneficial for those who have feelings of worthlessness and hopelessness, along with intense anxiety and restlessness.
Conclusion:
On World Suicide Prevention Day, let us come together as a global community to create hope through action. By breaking the silence, learning the warning signs, offering support, and advocating for change, we can make a profound difference in the lives of those struggling with suicidal thoughts. Remember, a small act of kindness and understanding can save a life and contribute to a world where hope prevails over despair. B Jain Pharmaceuticals plays a significant role in the holistic approach to addressing depression and suicidal thoughts through homeopathic remedies. While it is essential to remember that homeopathy is individualized and treats the whole person, B Jain Pharmaceuticals offers a range of homeopathic medicines that can be part of a comprehensive treatment plan. To Buy Homeopathic Medicines Online.

Dr Simranjit Kaur
Dr Simranjit Kaur is a highly accomplished medical professional with a BHMS degree from BVDU Pune and additional qualifications including CGO and MBA(Hospital Administration). With a passion for paediatric care, Dr. Simranjit pursed a fellowship in paediatrics, honing expertise in the specialized field. Currently Research Officer at BJain Pharmaceuticals.